Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 And 2 Pathophysiology

Diagnosis of conditions resembling type 2 diabetes chapters 13 3 4 and 13 3 5 and the pathophysiology of hypertension macro and microvascular disease chapters 13 5 13 6 1 and 13 6 4 and the role of genetic factors in the aetiology of type 2 diabetes chapter 13 3 1 are described in detail elsewhere.
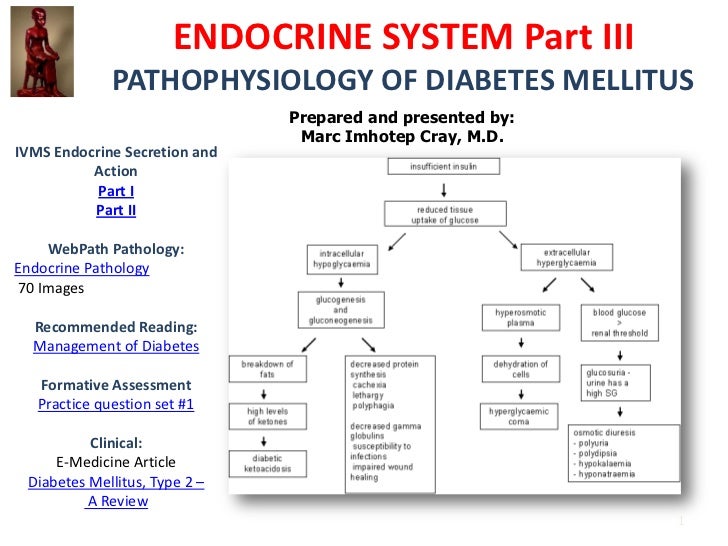
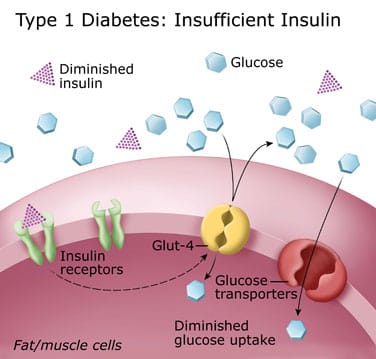
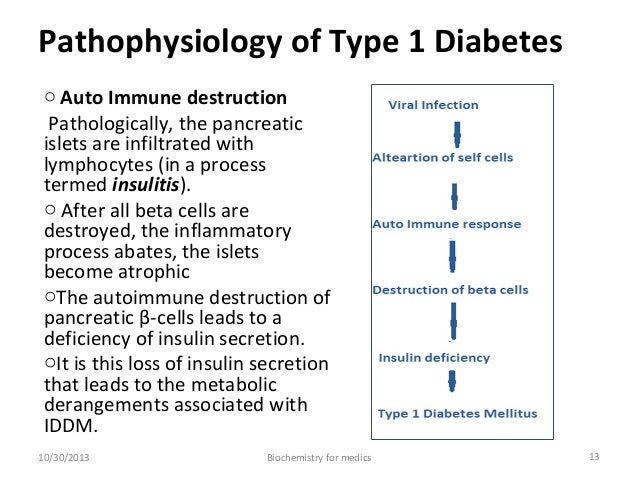
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 pathophysiology. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia and insulin deficiency resulting from the loss of beta cells in pancreatic islets mapes faulds 2014. Find out here about the differences and similarities including the symptoms. Nonimmune type 1b diabetes occurs secondary to other diseases and is much less common than autoimmune type 1a. Pathophysiology of diabetes type 1.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are shown in table 2. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both relate to the body s use of insulin but they have different causes and treatment. Continued type 2 diabetes. Usually the body s own immune system which normally fights harmful bacteria and viruses mistakenly destroys the insulin producing islet or islets of langerhans cells in the pancreas.
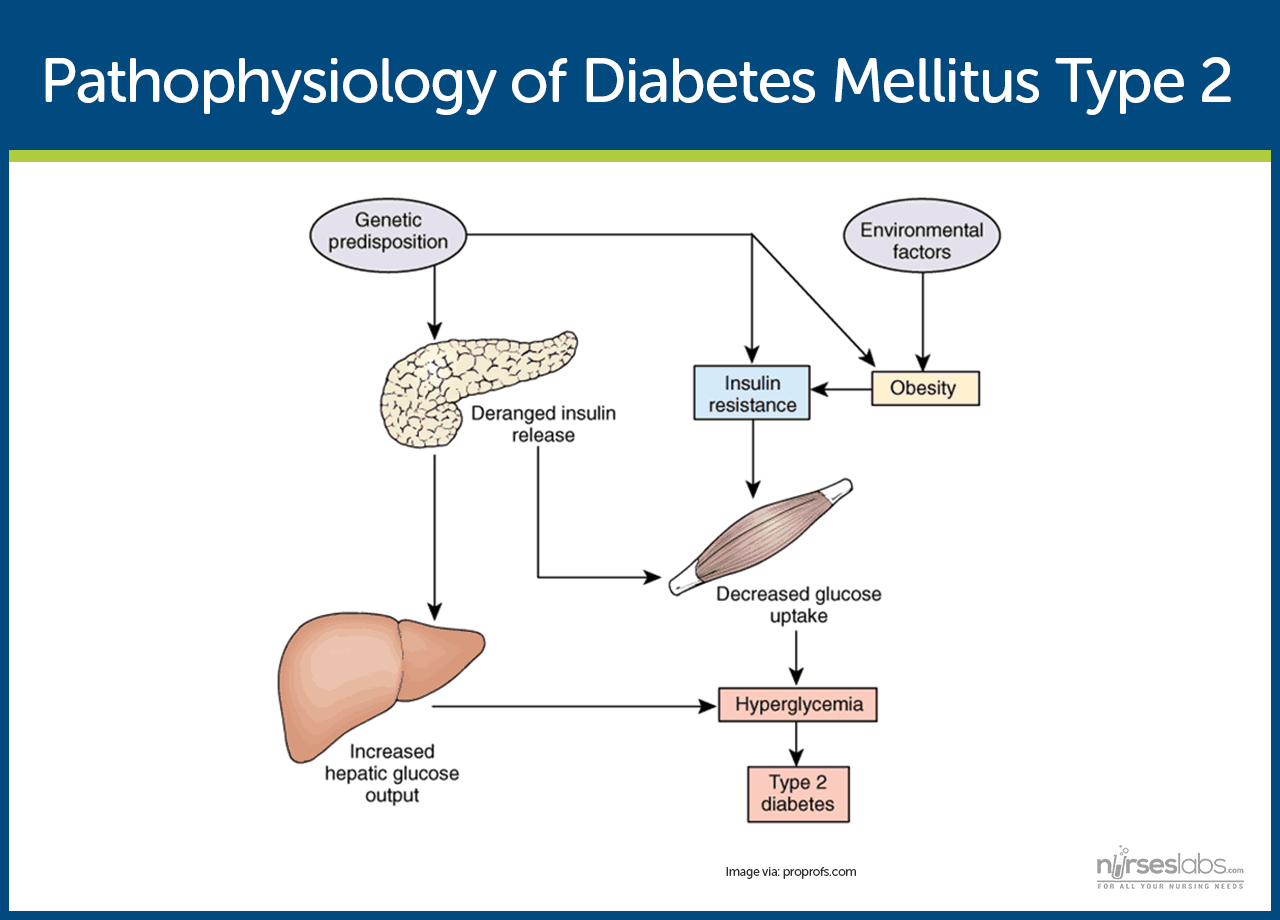
Causes of type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous syndrome characterized by abnormalities in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Type i diabetes mellitus formerly referred to as juvenile onset diabetes mellitus or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. The body s immune system is responsible for fighting off.
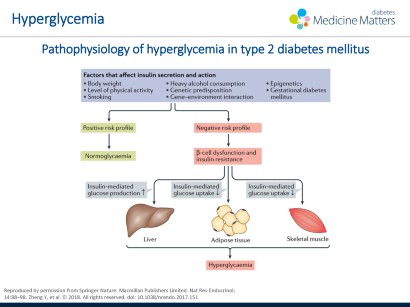
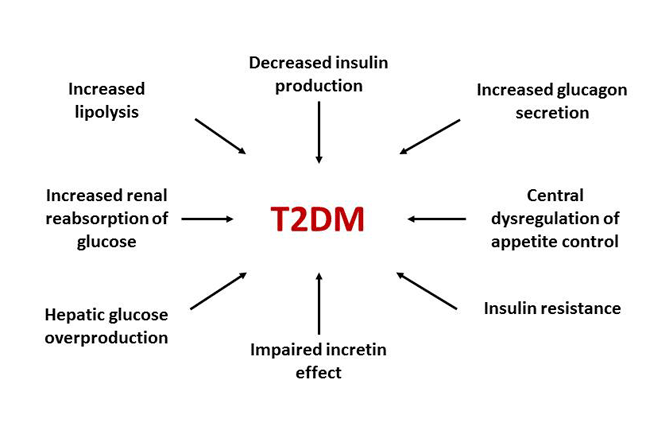
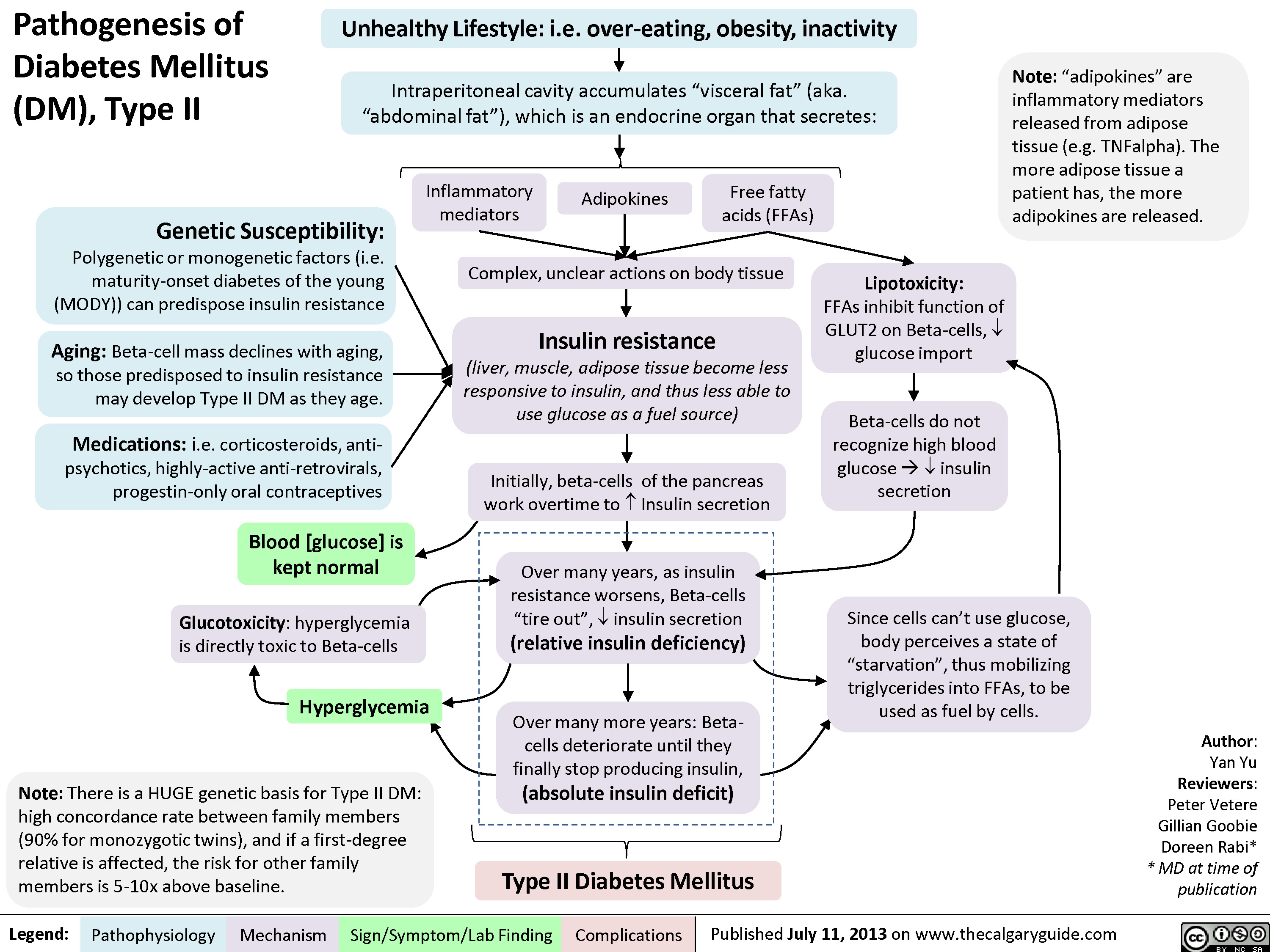
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have similar names but they re different diseases with unique causes. The causes of type 2 diabetes are multi factorial and include both genetic and environmental elements that affect beta cell function and tissue muscle liver adipose tissue pancreas insulin sensitivity. Although type 1 diabetes affects all age groups the. Type 2 diabetes used to be called non insulin dependent or adult onset diabetes but it s become more common in children and teens over the past 20 years largely.
Epidemiology and etiology of type 1 diabetes iddm type 1 diabetes represents around 10 of all cases of diabetes affecting approximately 20 million people worldwide american diabetes association 2001.