How Does Insulin Cause Hypokalemia

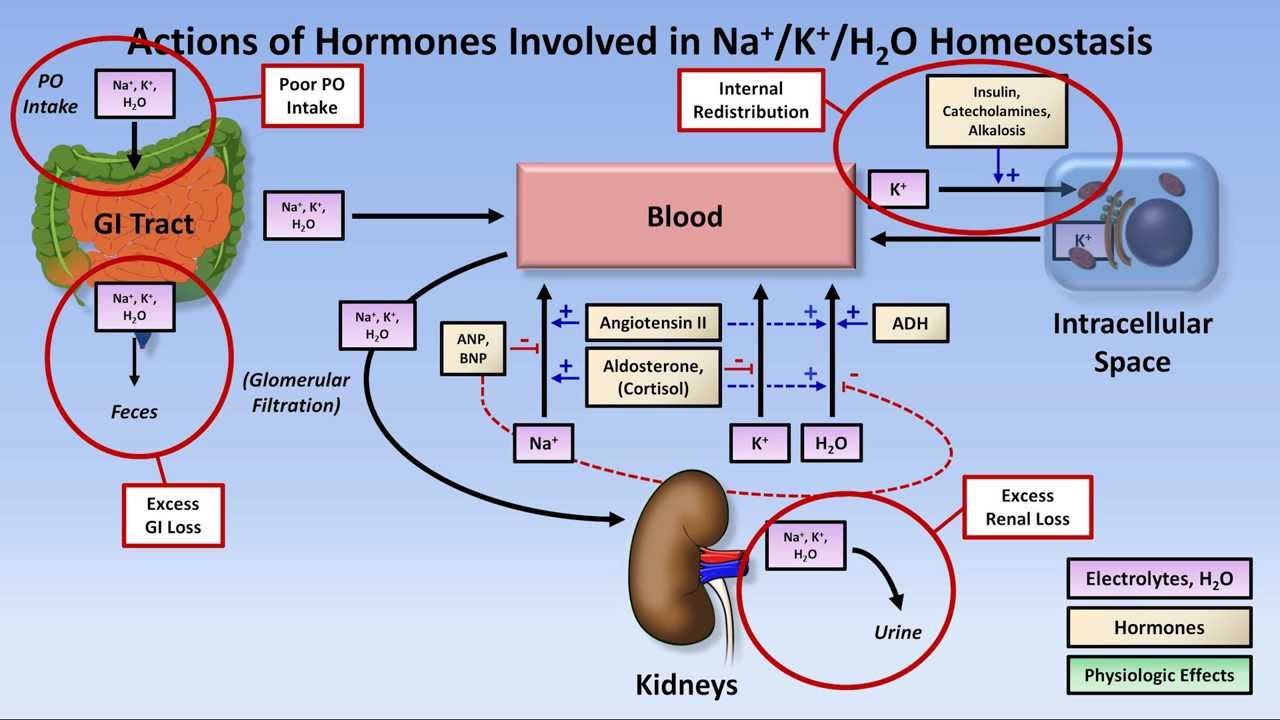
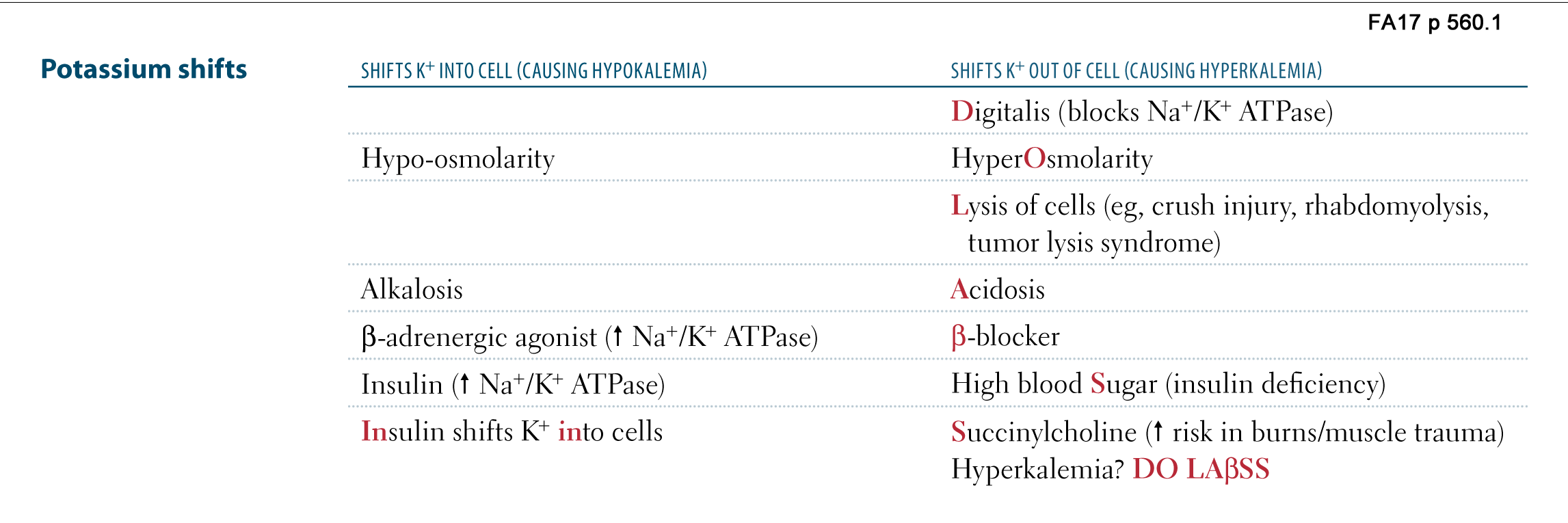
Insulin suppresses the breakdown and buildup of glycogen which is the storage form of glucose it blocks fat metabolism and the release of fatty acids and it puts potassium into the cells by activating the sodium potassium cellular channels.
How does insulin cause hypokalemia. This was the best explanation of why it happens that i could find and seems to be tied to atp activity. Insulin has a number of actions on the body besides lowering your blood glucose levels. As part of your electrolytes that move in and out of the cells as needed. Potassium levels are decreased by insulin.
Insulin reduces serum k from ecf to icf mainly because insulin increases the activity of th. Electrolyte imbalance is a common problem for people with diabetes. When you have too much glucose in your blood your kidneys start to filter the glucose out from the body through urine including other ions such as potassium phosphates and magnesium leading to hypokalemia hypophosphatemia and hypomagnesemia e g low levels of these ions. Certain drugs or conditions may cause your kidneys to excrete excess potassium.
So insulin only shifts the k from the extracellular compartment to the intracellular compartment it doesn t decrease the total k content of the body remember it that s why during management of hyperkalemia 1st initial therapy is done by giving insulin glucose combination which usually needs 30 minutes. Studies show that people with low potassium levels release less insulin have higher blood sugar levels and are more likely to get type 2 diabetes than those with normal potassium levels. Hypokalemia suppresses insulin release leading to glucose intolerance. Dextrose intravenous fluids stimulate the insulin secretion causing the shift of extracellular potassium into the cells by activating cell membrane na k atpase pump.
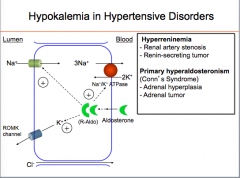
The relationship between insulin and potassium shortly after insulin was discovered scientists revealed that insulin had something to do with the potassium levels in both the cells and in the blood. Trauma or insulin excess especially if diabetic can cause a shift of potassium into cells hypokalemia. Insulin is the first line defense against hyperkalemia. A person can have low potassium hypokalemia or high potassium hyperkalemia both of which are asymptomatic conditions that can be serious as they both cause heart arrhythmias.
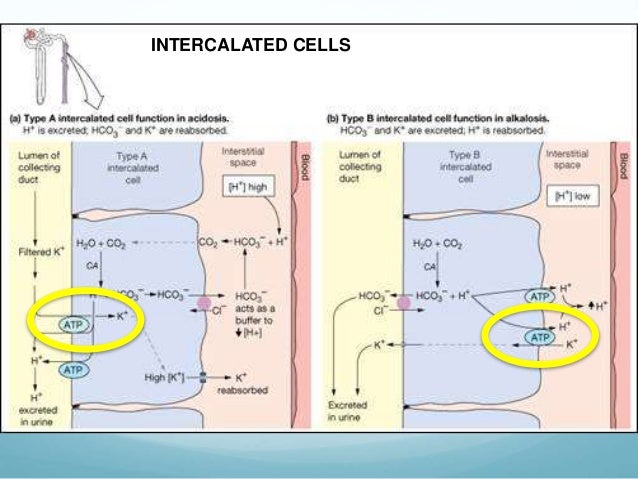
Your potassium level is maintained within a range. A person can have low potassium hypokalemia or high potassium hyperkalemia both of which are asymptomatic conditions that can be serious as they both cause heart arrhythmias. Insulin results hypokalemia just by increasing the activity of h k atpase pump. Potassium is excreted or flushed out of your system by your kidneys.
Hypokalemia is low potassium. How does diabetes cause hypokalemia.