Hierarchy Of Superior Court In Malaysia
These are those courts in malaysia which are somewhat similar to the former quarter sessions in england.
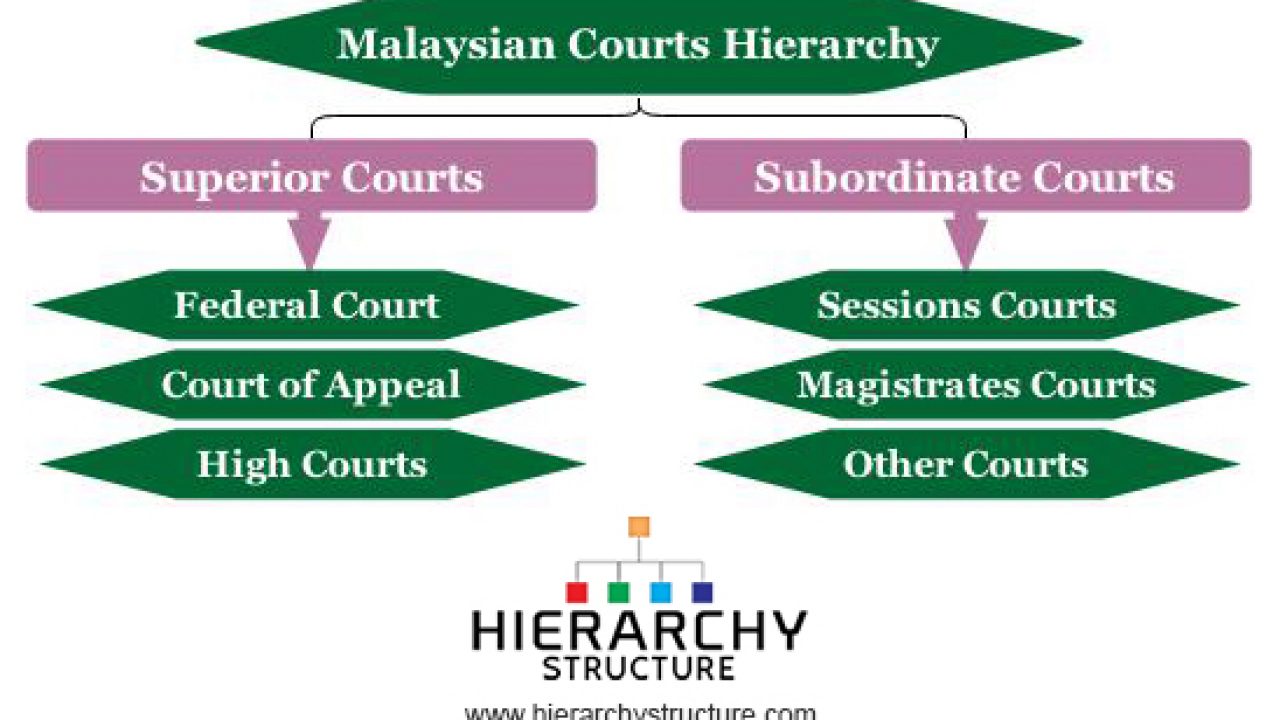
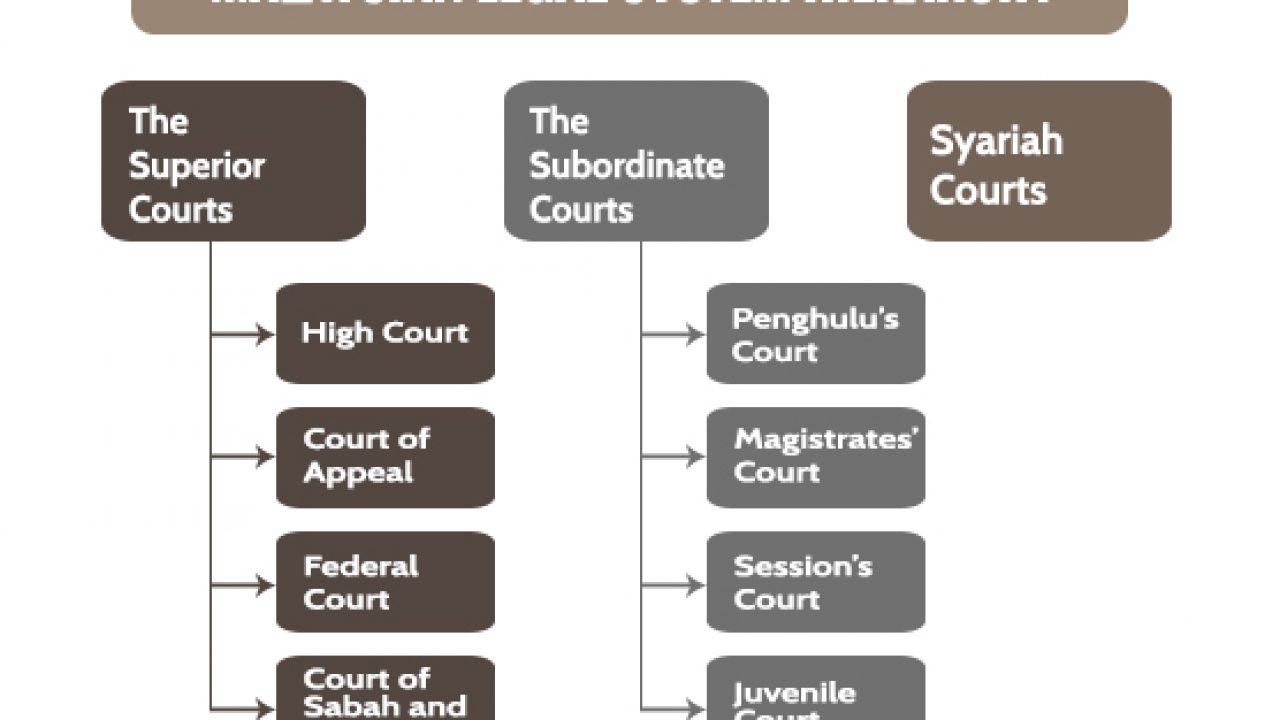
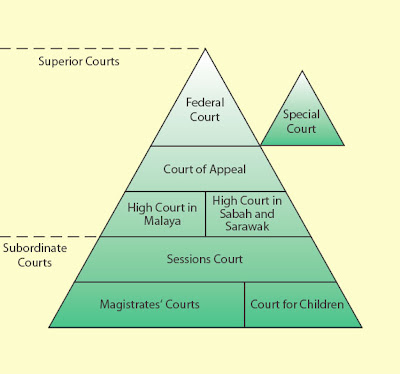
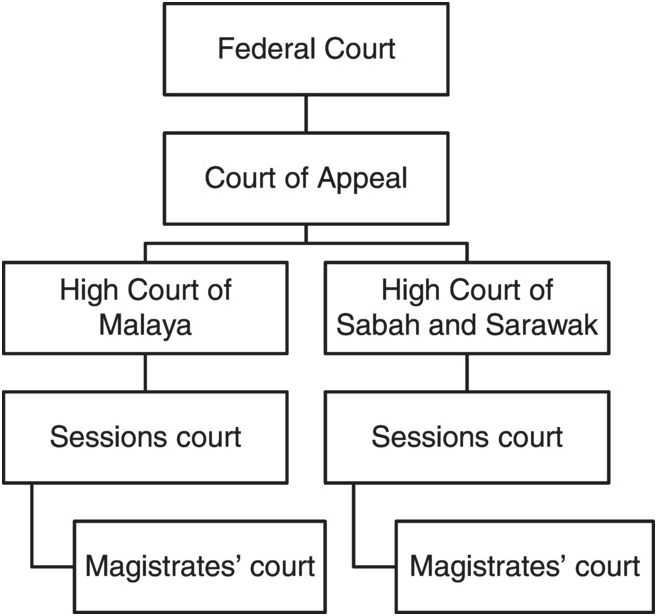
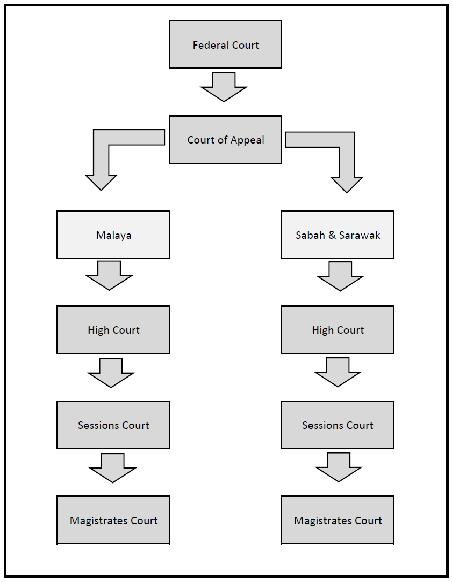
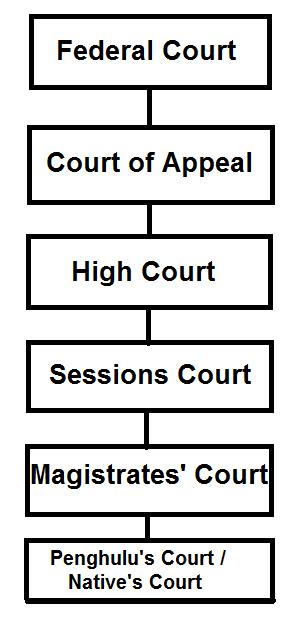
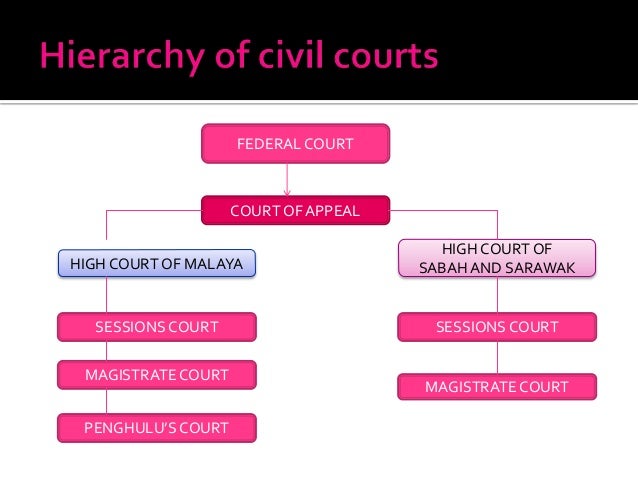
Hierarchy of superior court in malaysia. Penghulu s court the penghulu s courts hear civil issues in which the claim is below rm50 00 and where the offenders are of asian race and speaks and understands the malay language. The hierarchy of courts begins from the magistrates court sessions court high court court of appeal and finally the federal court. The federal court of malaysia in the highest court of the land. The subordinate courts in malaysian legal system hierarchy the subordinate courts comprises the sessions courts the penghulu s courts in western part of malaysia and the magistrates court.
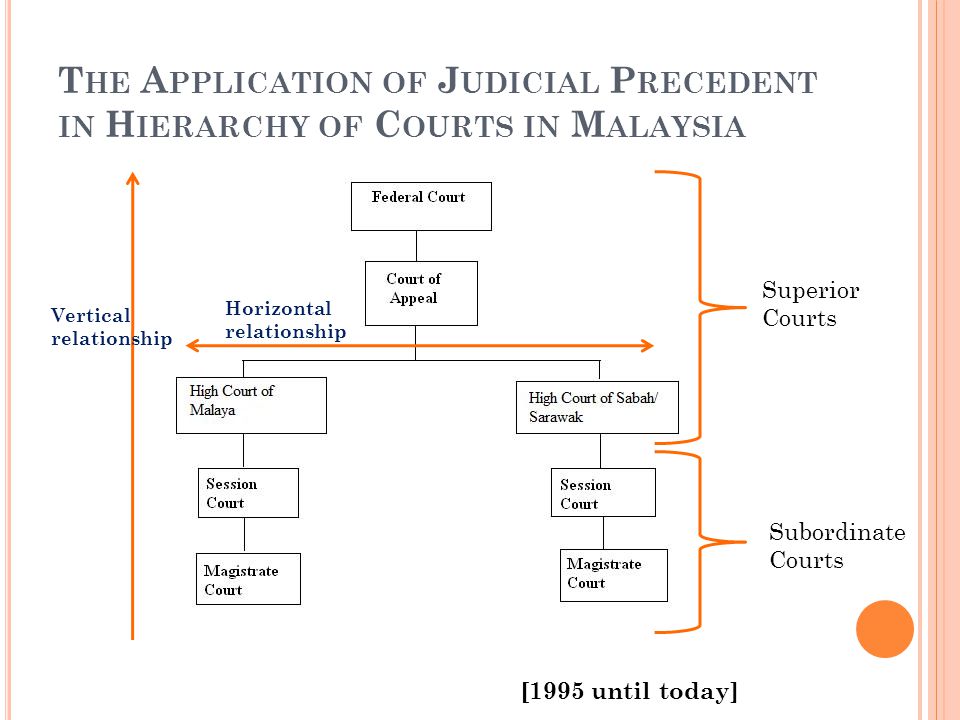
Judicial precedent is a system where a judge of a court makes a decision and the court at the same level as it or the courts below it in the hierarchy of the malaysian judicial system are bound to follow the decision make by it if the illegal point facts and situation in. The malaysian court system is organized in a hierarchy like a pyramid with the subordinate courts at the base and the superior courts at the top of the hierarchy. The following is the hierarchy of subordinate courts. Like how there is a court hierarchy for civil cases a similar hierarchy exists for criminal cases but it works in a slightly different manner.
Question 1 a in accordance with judicial precedent the judge of high court is bound to the decision of court of appeal. Before we kick things off a note to bear in mind is that we won t be covering the syariah courts or native courts in this article. The hierarchy of courts of malaysia starts with the magistrates court as the first level followed by the sessions court high court court of appeal and the federal court of malaysia. The judiciary of malaysia is largely centralized despite malaysia s federal constitution heavily influenced by the british common law and to a lesser extent islamic law and is mostly independent from political interference.
The jurisdiction of the courts in civil or criminal matters are contained in the subordinate courts act 1948 and the courts of judicature act 1964. The magistrates courts as well as the sessions courts in malaysia have jurisdiction in both civil and criminal matters. There are generally two types of trials criminal and civil. The first is in peninsular malaysia which contains forty five judges and judicial commissioners.